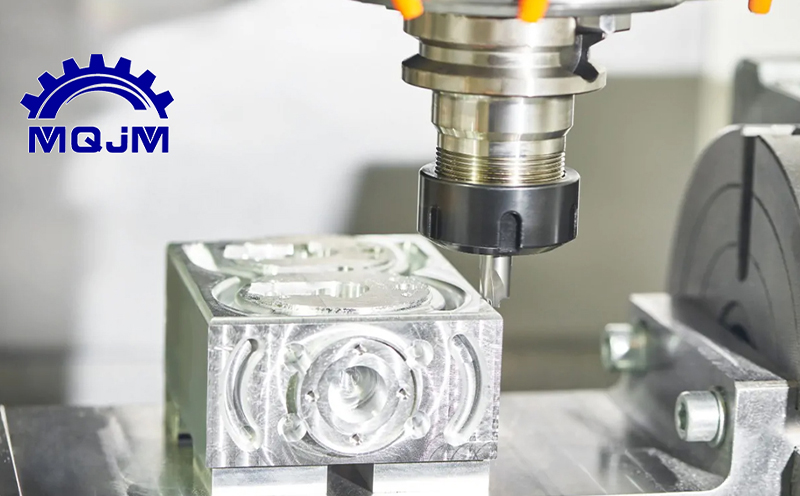
Surface finishing is the vital final step in CNC machining. It removes tool marks and other surface irregularities, improving both appearance and performance of machined parts. Proper finishing not only enhances cosmetic appeal (achieving smooth, consistent textures) but also adds protective layers that boost wear and corrosion resistance. For example, anodizing or coating a metal part can significantly extend its lifespan in harsh environments by preventing oxidation. In today’s competitive markets, flawless surface quality is essential: customers expect precision components that both look and function at a high standard.
Common CNC Surface treatments and Their Applications
Metal parts emerging from a CNC machine can receive a variety of finishing treatments, chosen based on material and end-use. Key processes include:
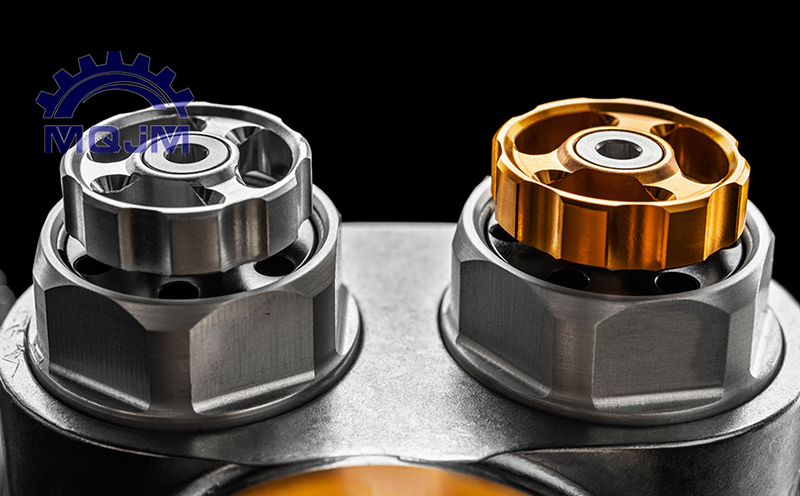
Anodizing: An electrochemical process applied mainly to aluminum and titanium parts. Anodizing converts the metal surface into a hard, corrosion-resistant oxide layer that can be dyed in many colors. This finish improves wear resistance and prevents rust. It’s widely used in aerospace, automotive, architecture and electronics, where durable, decorative CNC milling aluminum parts (frames, housings, panels) are needed. Type II (standard) anodizing gives a smooth finish and good corrosion protection, while Type III (hardcoat) produces a very thick, wear-resistant layer for heavy-duty applications.
Bead blasting (sandblasting): A mechanical process that bombards the part with tiny glass beads or abrasive grit, creating a uniform matte or satin texture. Bead blasting removes fine surface flaws and tool marks without altering basic dimensions significantly. It is primarily used for cosmetic finishing – for example, giving parts a uniform matte look for consumer goods, automotive trim, or industrial equipment. The result is a consistent appearance and a light “pearlized” texture. Because it is a manual process, results can vary slightly by operator, but it’s a low-cost way to improve aesthetics without adding material.
Electroplating: This covers a part’s surface with a thin layer of metal (such as nickel, chrome, zinc, or copper). Plating “beautifies” parts, prevents rust, and can improve properties like electrical conductivity. For instance, chrome plating on steel parts adds shine and corrosion protection, while nickel plating provides wear resistance and good solderability for electronic components. Most metals and alloys (steel, brass, aluminum, copper, etc.) can be electroplated as long as they are conductive. Common applications include automotive hardware, consumer electronics connectors, plumbing fixtures, and decorative industrial components.
Powder Coating: A durable polymer finish applied as a dry powder and then cured under heat. Powder coating creates a hard, wear- and corrosion-resistant surface on metal parts. It offers high impact strength (stronger than anodized finishes) and comes in many colors. Because it requires baking the part (typically ~200 °C), it’s used on metals that can tolerate heat. Powder coating is popular for outdoor or heavy-duty parts such as automotive body panels, steel furniture, architectural aluminum extrusions, and machinery housings. The result is a smooth, protective finish that resists chipping and environmental damage.
Polishing: uses abrasive wheels, compounds or even electrochemical action to smooth and shine a part's surface. It reduces surface roughness and creates a mirror-like finish. This process is suitable for all metals and even some plastics. Polished finishes are used where appearance or tight tolerances matter – e.g. consumer products (jewelry, hardware), optics, medical devices, and stainless steel food/CNC medical parts. For example, polishing stainless steel impellers or aluminum housings gives a clean, reflective look. (Electropolishing, a related method, is often used for stainless steel medical parts to achieve ultra-smooth, sterile surfaces.)
Passivation: (often combined with polishing) This is a chemical treatment for stainless steel and other alloys. Passivation (using nitric or citric acid) removes free iron from the surface and creates a thin protective oxide layer. The result is greatly improved corrosion resistance and long-term cleanliness. Passivation is critical for aerospace, medical, and food-industry parts, where stainless components (bolts, tubing, fittings) must be highly resistant to rust and contaminants.
etc............

Each finishing method is selected for specific materials and industries. For example, anodizing is restricted to aluminum/titanium parts (think aerospace structural parts or consumer electronics enclosures), whereas plating can cover many metals (common in automotive, industrial hardware, electronic connectors). Bead blasting and polishing work on virtually any material to improve aesthetics (used in automotive interiors, prototypes, architectural fittings, etc.). Powder coating suits heavy steel or aluminum parts in construction, appliances and transportation. By matching finish to material and use-case, manufacturers ensure parts meet the strict functional and visual requirements of their industries.
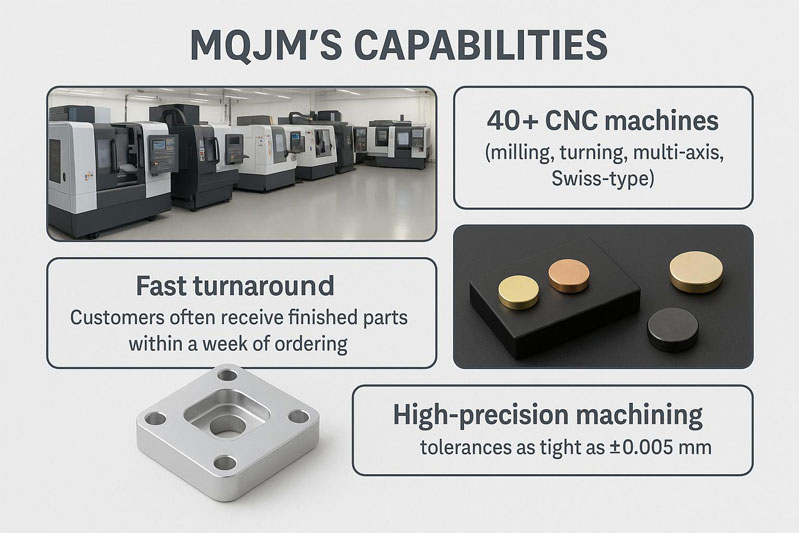
MQJM’s Capabilities
With 40+ CNC machines (milling, turning, multi-axis, Swiss-type) in-house, MQJM can produce complex parts quickly. This capacity enables fast turnaround times – customers often receive finished parts within a week of ordering. MQJM works with 40+ certified materials (various grades of aluminum, steel, brass, copper, plastics, etc.), so virtually any requested alloy can be machined and finished. High-precision machining is a strength: MQJM routinely achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. These capabilities allow MQJM to deliver large or small batches of precision components with consistent quality.
By combining cutting-edge machinery with strict inspection procedures and versatile finishing processes, MQJM ensures that your parts meet the highest standards. The result is reliable, repeatable quality that supports B2B customers in fields like automotive, electronics, aerospace and more. MQJM’s extensive capabilities and customer-centric approach make it a strong partner for companies needing CNC precision machining parts with superior surface finishes.
Contact MQJM today to discuss your project with custom CNC precision machining and excellent surface treatments!